Offensive Strategies

China Expertise
Understanding China’s role in emerging technologies is vital for navigating a complex global environment where technology shapes economies, politics and societies. China’s rapid advancements in AI, 5G, biotechnology and more drive innovation and reshape industries, influencing economic competitiveness and strategic power dynamics. As China establishes itself as a tech leader, comprehension of its strategies, investments, and regulations becomes crucial for informed decision-making.

Development Finance
Development finance is a pivotal arena in the ongoing rivalry between the United States and China. This landscape is defined by divergent strategies in capital investment, reflecting contrasting visions of global influence. China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is an example of China’s approach, funneling substantial funds into infrastructure projects across Asia, Africa and beyond. In contrast, the U.S. pursues development finance through institutions like the Overseas Private Investment Corporation (OPIC) and the newly established U.S. International Development Finance Corporation (DFC), focusing on fostering economic growth and stability.

Diplomacy
As emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, 5G networks and biotechnology reshape the global landscape, diplomatic efforts play a pivotal role in managing tensions, fostering collaboration and establishing norms. Diplomacy involves the art of negotiation, communication and cooperation between nations to address shared challenges and opportunities.

Education
Higher education has become a space for competition for academic excellence, innovation and global influence. This includes efforts to attract international students, foster cutting-edge research and cultivate intellectual leadership. Higher education encompasses academic collaboration, knowledge dissemination and cultural exchange between nations. Notably, American universities have long been global magnets for talent and research funding, fostering innovation hubs like Silicon Valley.

Lawfare
Lawfare is the use of legal mechanisms and strategies to achieve strategic goals, including those that influence international relations and technology-related disputes. As emerging technologies like cyber warfare, intellectual property disputes and data privacy challenges emerge, the legal arena becomes a crucial battleground for asserting influence and securing advantages. Both the U.S. and China employ legal tools to pursue various goals: the U.S. emphasizes its legal framework to address cybersecurity concerns and protect intellectual property, while China’s “Legal Warfare” doctrine integrates legal mechanisms into its broader strategies.

Logistics
Logistics plays a pivotal role in the ongoing technological rivalry between the United States and China. As these global tech powerhouses strive for dominance, efficient logistics systems have emerged as critical enablers. Both countries are vying to enhance supply chain efficiency, reduce manufacturing lead times, and optimize distribution networks.

Microlending
Microfinance is a means of empowering individual entrepreneurs in both urban and rural areas, providing capital to grow businesses and livelihoods at scale in a sustainable and replicable model. The benefits flow to the entrepreneur themselves, their families and communities, and the broader society and economy in their country. Every successful business or farm produces income, often contributes to the tax base, and reduces government support needs.

Military-Civil Fusion
In today’s era of rapid technological evolution, military-civil fusion is of paramount importance. It enables nations to efficiently harness innovation, ensuring that technological progress benefits both defense and civilian sectors. This approach fosters collaboration between academia, research institutions and private companies, creating a synergistic ecosystem. By pooling resources, expertise and infrastructure, military-civil fusion accelerates technological breakthroughs, strengthens national security, and boosts economic competitiveness in a way that aligns security interests with broader societal advancements.

Outbound Investment
In the present era marked by rapid technological advancements, outbound investment in emerging technologies holds significant importance. Outbound investment involves directing investments from one country to another to capitalize on innovative technologies and business opportunities. This field encompasses the strategic allocation of capital to acquire or partner with foreign tech companies, gain access to new markets and foster international collaboration in emerging tech sectors.

Prosperity Partnerships
Prosperity partnerships are collaborative endeavors between businesses, governments, and civil society aimed at harnessing technological innovations to drive economic growth, social well-being, and sustainable development. In an era marked by rapid technological advancements, these partnerships have gained paramount importance. They foster cross-sectoral cooperation to address complex challenges such as equitable access to digital infrastructure, upskilling the workforce for tech-intensive jobs, and promoting ethical practices in areas like artificial intelligence and biotechnology.

Venture Investing
With emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, quantum computing and biotechnology driving transformative changes, investment screening is pivotal to protect sensitive intellectual property, prevent technology leakage and maintain strategic advantage. Its importance is heightened by the potential for foreign acquisitions to enable undue influence or transfer critical technologies.

Social Credit Rating System
China’s Social Credit System is a national credit rating and blacklist being developed by the government of the People’s Republic of China. The system tracks businesses, individuals and government institutions and evaluates them for trustworthiness. Supporters claim that the system helps to regulate social behavior, improve the perceived “trustworthiness” of citizens (which includes paying taxes and bills on time), and promote traditional Chinese moral values.
Defensive Strategies

Diplomacy
As emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, 5G networks and biotechnology reshape the global landscape, diplomatic efforts play a pivotal role in managing tensions, fostering collaboration and establishing norms. Diplomacy involves the art of negotiation, communication and cooperation between nations to address shared challenges and opportunities.

Logistics
Logistics plays a pivotal role in the ongoing technological rivalry between the United States and China. As these global tech powerhouses strive for dominance, efficient logistics systems have emerged as critical enablers. Both countries are vying to enhance supply chain efficiency, reduce manufacturing lead times, and optimize distribution networks.

Board Strategy
Board strategy involves the decision-making and governance practices of corporate boards, particularly in relation to navigating challenges and opportunities posed by emerging technologies. As sectors like artificial intelligence, quantum computing and biotechnology transform industries, boards are tasked with making informed choices that align with competitive advantage, ethical considerations and geopolitical dynamics. While U.S. companies emphasize shareholder value and market responsiveness, Chinese firms often align with government objectives and long-term growth.

Capital Markets
American investors are unknowingly financing the CCP’s human rights abuses, surveillance state, and military-civil fusion because the CCP has infiltrated American capital markets through the back door. They’ve managed to get around the financial transparency laws that American and other companies must follow in order to enjoy the same access, and are often buried in various index bonds, which are then incorporated into hundreds of products, ETFs, and mutual funds.
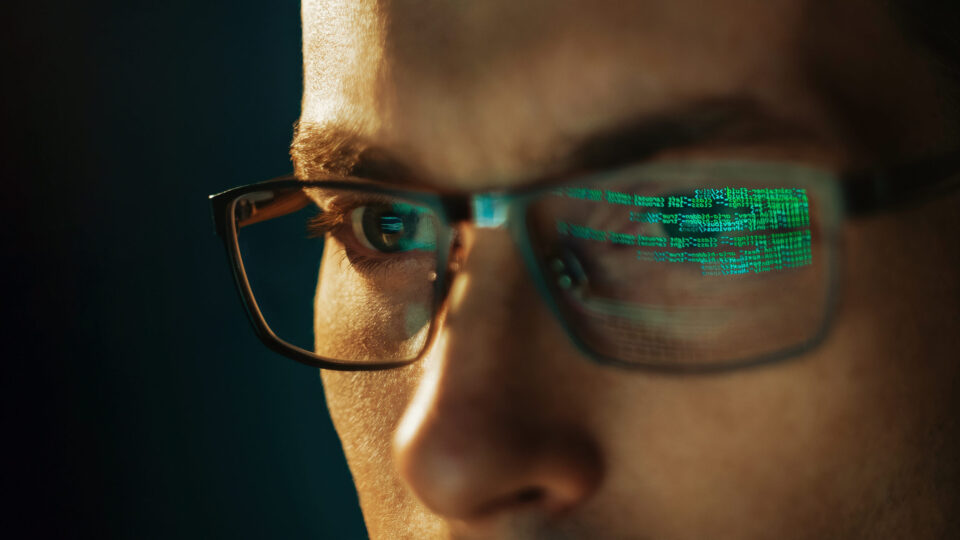

Data and Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity has become a race to secure sensitive information and critical infrastructure, with profound global implications. The increasing reliance on digital systems and the rapid development of emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and 5G have amplified the importance of safeguarding data and cyber infrastructure. As emerging technologies become more interconnected and pervasive, the attack surface for cybercriminals widens.
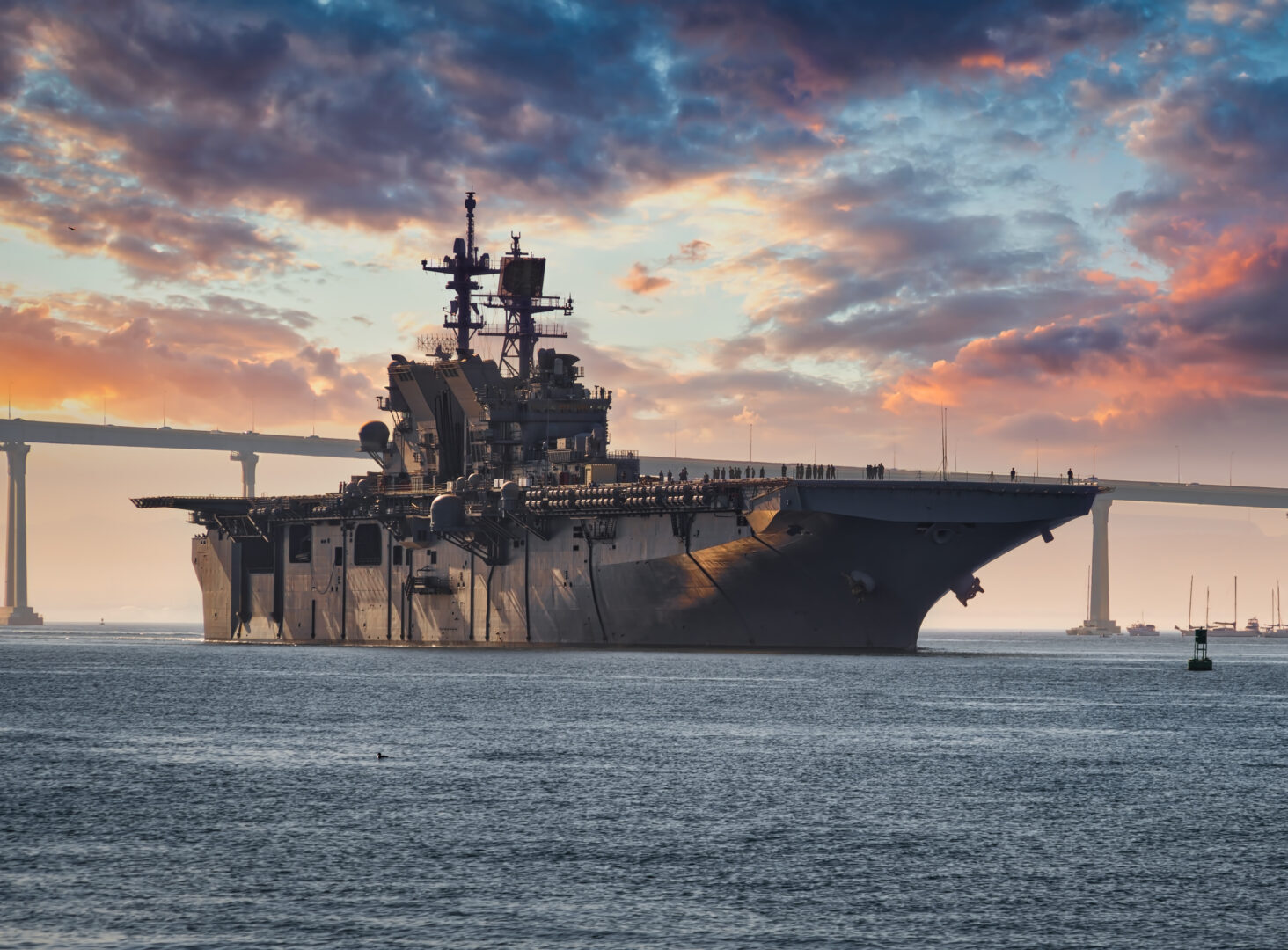

Defense
Defense plays a pivotal role in the global tech competition between the US and China. As these technological powerhouses vie for dominance, the significance of safeguarding intellectual property, critical infrastructure, and sensitive data cannot be overstated. Cutting-edge advancements in areas like artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and 5G networks have dual-use applications, both for civilian innovation and military capabilities. The ability to protect and defend these technologies is essential to maintaining a competitive edge and national security.

Economic Security
As emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, quantum computing and advanced manufacturing reshape industries, concerns arise about economic competitiveness, market dominance and supply chain vulnerabilities. China’s strategic investments in these sectors, often driven by state-driven initiatives, have prompted debates over fair competition, intellectual property protection, and technological sovereignty.

Export Controls
All US financial institutions have a duty to establish governance principles when it comes to investing in entities that directly or indirectly facilitate human rights abuses. The boards of these institutions have a moral duty, and perhaps even a fiduciary duty to divest from companies that contribute to human rights violations.
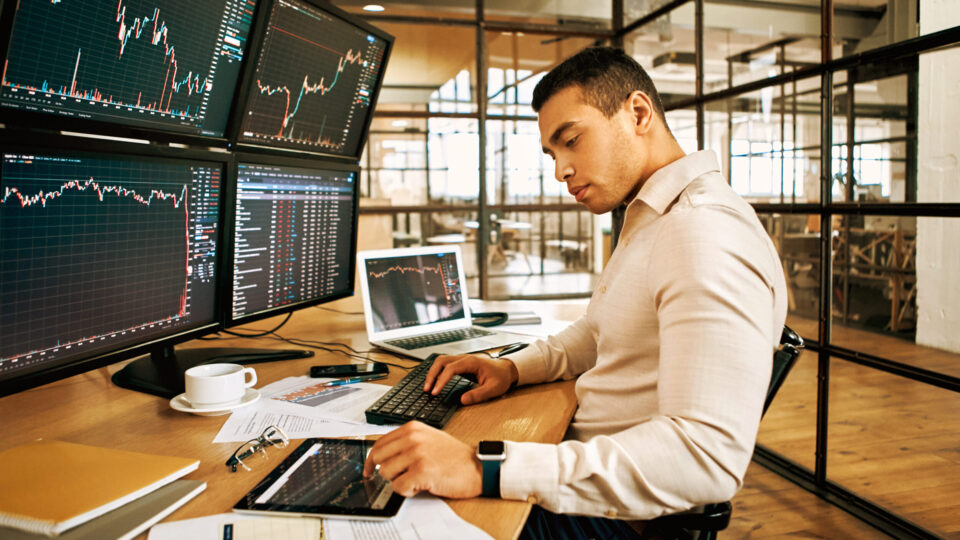

Investment Screening
With emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, quantum computing and biotechnology driving transformative changes, investment screening is pivotal to protect sensitive intellectual property, prevent technology leakage and maintain strategic advantage. Its importance is heightened by the potential for foreign acquisitions to enable undue influence or transfer critical technologies.

IP Protection
The Global Tech Security Commission is focused on the urgent mission of securing high tech from growing techno-authoritarian threats. The Commission also has the support of lawmakers and private-sector leaders at a time when the United States is working to unite its Transatlantic and Indo-Pacific allies and partners across a range of critical technology issues.

Media / Disinformation
Media has come to play a pivotal role in shaping narratives, projecting soft power and influencing global perceptions. It encompasses the creation, distribution and consumption of information and entertainment, and its landscape is rapidly evolving due to emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, virtual reality and blockchain. These technologies are reshaping how content is produced, delivered and experienced. For example, AI-powered algorithms curate personalized news feeds potentially reinforcing filter bubbles and altering information consumption patterns. Virtual reality enables immersive storytelling, transforming the way audiences engage with narratives. Meanwhile, blockchain can enhance transparency and trust in content verification and distribution.
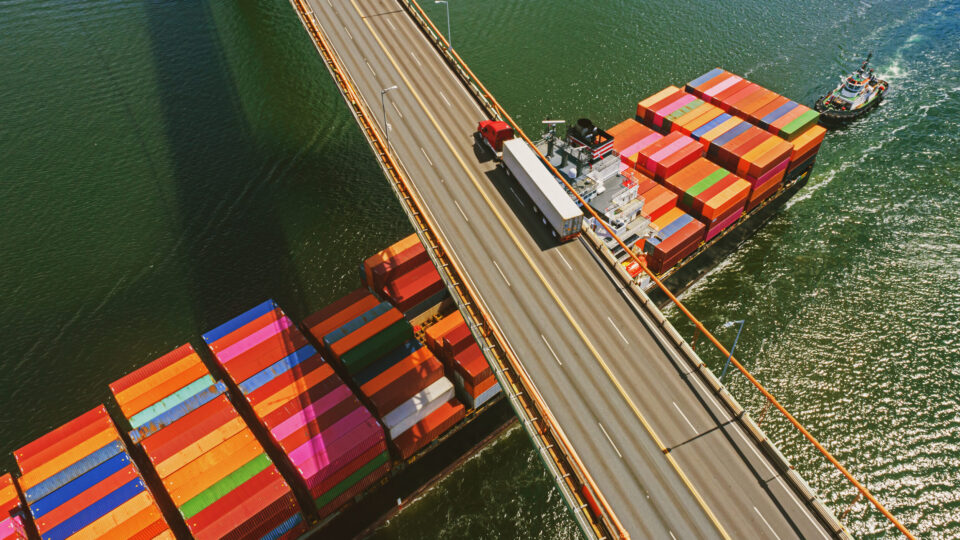

Supply Chains
The topic of supply chain management has become central to the U.S.-China economic relationship, as it touches every single tech sector. Supply chain management involves the design, coordination and optimization of processes that govern the flow of goods, services and information. Notably, China’s role as a manufacturing hub and its dominance in various supply chain nodes, like electronics and textiles, highlights its strategic position.
Force Multipliers

Global Trusted Tech Network
The Global Trusted Tech Network comprises like-minded countries, companies, and civil society that operate by a set of democratic values and trust principles for all areas of collaboration. It is an alliance of democracies built on the idea that strong partnerships advance shared prosperity. Partnerships are grounded in democratic values and shared Trust Principles that form the basis of trust: integrity, accountability, transparency, reciprocity and respect for the rule of law, property, and sovereignty.

Models and Doctrines
The ‘Trust Principle’ doctrine of collaboration is engineered to advance freedom through trust-based alliances. China’s techno-economic aggression presents a serious threat to the free world, especially when it comes to advanced technologies. The Clean Network pioneered a trust-based model for countering authoritarian aggression across all areas of techno-economic competition.
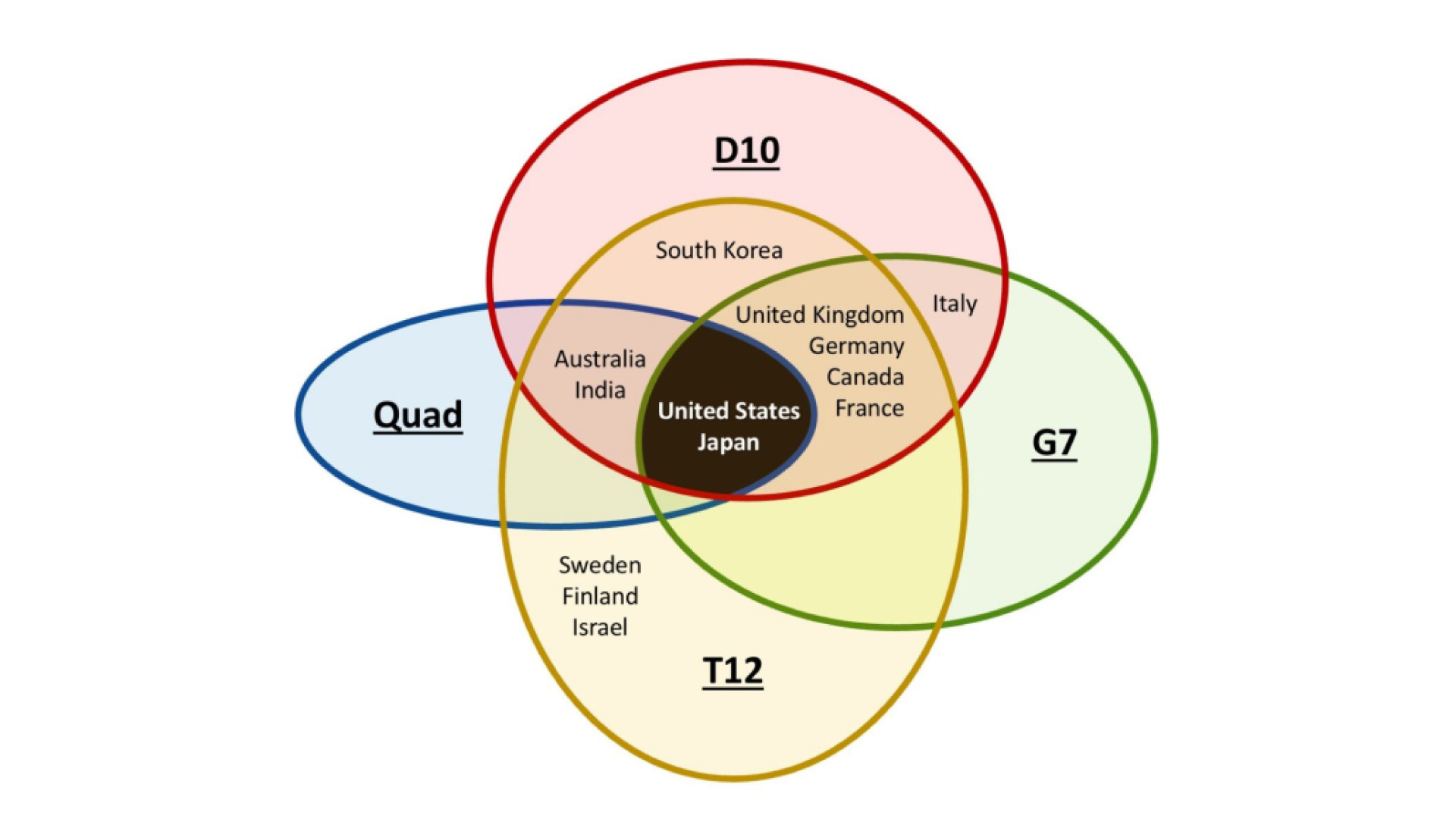
Coalitions
International coalitions and alliances are a vital way for democratic nations to ally together and support one another against authoritarian regimes. Four coalitions that are key to tech diplomacy include: The Quad — Geostrategic, G7 — Economic, T12 –Technological, D10 — Governance.

International Organizations
Leveraging the existing networks of international organizations can be powerful force accelerators in the creation of alliances to stand against tech authoritarianism.

Private Sector Organizations
Civil Society Organizations (CSOs), Companies and Industry Associations, Academia
Authoritarian Strategies

Lawfare
Lawfare is the use of legal mechanisms and strategies to achieve strategic goals, including those that influence international relations and technology-related disputes. As emerging technologies like cyber warfare, intellectual property disputes and data privacy challenges emerge, the legal arena becomes a crucial battleground for asserting influence and securing advantages. Both the U.S. and China employ legal tools to pursue various goals: the U.S. emphasizes its legal framework to address cybersecurity concerns and protect intellectual property, while China’s “Legal Warfare” doctrine integrates legal mechanisms into its broader strategies.
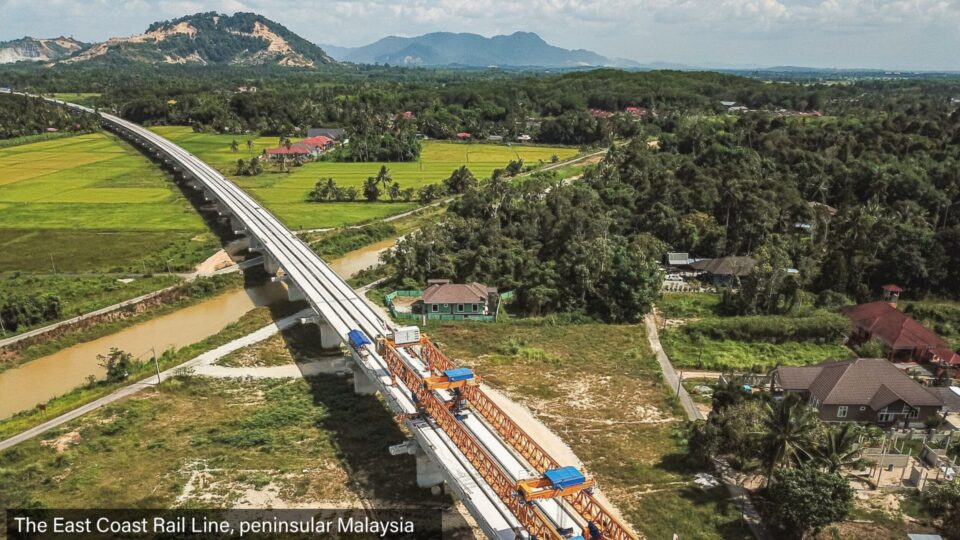

One Belt One Road
China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), formerly known as One Belt One Road, is a global infrastructure development strategy adopted by the Chinese government in 2013 to invest in nearly 150 countries and international organizations. It is considered a centerpiece of the Chinese leader Xi Jinping’s foreign policy, which calls for China to assume a greater leadership role for global affairs in accordance with its rising power and status.
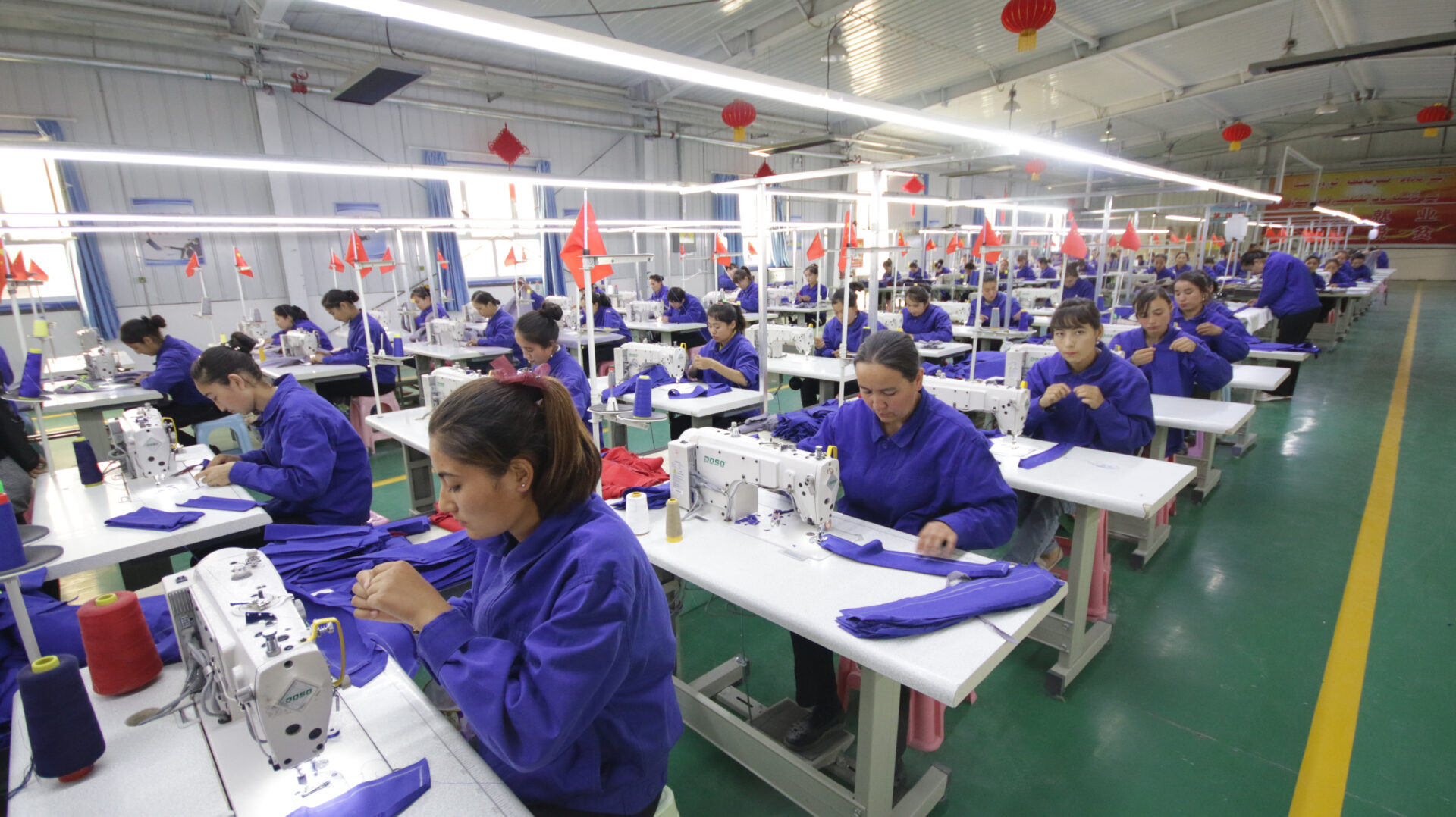

Forced Labor
The United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) released a long-awaited report on Aug. 31, 2022 on Chinese government abuses in Xinjiang. Broadly, the report concluded that “serious human rights violations have been committed,” including “arbitrary and discriminatory detention of members of Uyghur and other predominantly Muslim groups,” which it asserted “may constitute international crimes, in particular crimes against humanity.”

Social Credit Rating System
China’s Social Credit System is a national credit rating and blacklist being developed by the government of the People’s Republic of China. The system tracks businesses, individuals and government institutions and evaluates them for trustworthiness. Supporters claim that the system helps to regulate social behavior, improve the perceived “trustworthiness” of citizens (which includes paying taxes and bills on time), and promote traditional Chinese moral values.

Capital Markets
Today, US businesses seeking capital on our stock exchanges are subject to strict domestic security laws. But foreign companies do not have to comply with these standards if their domestic regulators do not require them to. Almost all countries have comparable transparency standards, but China stands out as an exception. This sets the perfect environment for financial fraud on a broad scale.


